HTTP请求传参详解
本篇文章主要介绍了HTTP的数据结构, 以及application/x-www-form-urlencoded,multipart/form-data, application/json类型请求的编码方式。
什么是HTTP
HTTP(超文本传输协议) 是服务器和客户端之间交换数据的方式。是为Web浏览器与Web服务器之间的通信而设计的有两种类型的消息︰
- 请求(requests)– 由客户端发送用来触发一个服务器上的动作;
- 响应(responses)– 来自服务器的应答。
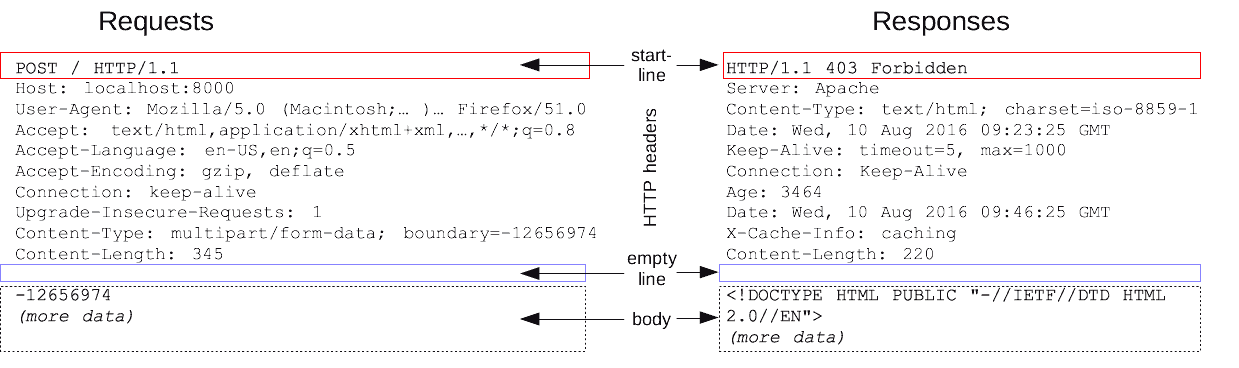
HTTP请求和响应具有相似的结构,由以下部分组成︰
- 一行起始行用于描述要执行的请求,或者是对应的状态,成功或失败。这个起始行总是单行的。
- 一个可选的 HTTP 头集合指明请求或描述消息正文。
- 一个空行指示所有关于请求的元数据已经发送完毕。
- 一个可选的包含请求相关数据的正文 (比如 HTML 表单内容), 或者响应相关的文档。 正文的大小有起始行的
HTTP头来指定。
起始行和 HTTP 消息中的 HTTP 头统称为请求头,而其有效负载被称为消息正文。
HTTP规范
HTTP 定义了一组请求方法,以表明要对给定资源执行的操作。包括
GET: 请求一个指定资源的表示形式,使用 GET 的请求应该只被用于获取数据。HEAD: 请求一个与 GET 请求的响应相同的响应,但没有响应体。POST: 用于将实体提交到指定的资源,通常导致在服务器上的状态变化或副作用。PUT: 用请求有效载荷替换目标资源的所有当前表示。DELETE: 删除指定的资源。CONNECTCONNECT: 建立一个到由目标资源标识的服务器的隧道。OPTIONS: 用于描述目标资源的通信选项。TRACE: 沿着到目标资源的路径执行一个消息环回测试。PATCH: 用于对资源应用部分修改。

请求传参的几种方式
URL传参(Query String )
Query String是URL的一部分,采用百分比编码的方式,我们可以通过?开头并用&符号分隔的键-值对,同时以=分隔键和值, 如http://test.com?key1=value1&key2=value2来提供额外参数。为了方便构造查询字符串,我们可以使用URLSearchParams构造
// 传入字符串
new URLSearchParams(`key1=value1&key2=value2`).toString() // key1=value1&key2=value2
// 传入数组
new URLSearchParams([["key1", "value1"],["key2", "value2"]]); // key1=value1&key2=value2
// 传入对象
new URLSearchParams({"key1" : "value1", "key2" : "value2"});
// 通过URL传入的参数都会被隐式地转译为百分比编码的`字符串`, 如果保护有特殊字符将被转译,非字母或数字的字符会被 percent-encoding<https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/percent-encoding>
new URLSearchParams(`key1=1,2,3`) // key1=1%2C2%2C3 即 key1=1,2,3
new URLSearchParams([["key1", [1,2,3]]]); // key1=1%2C2%2C3 即 key1=1,2,3,数组被隐式转换为1,2,3
new URLSearchParams({"key1" : [1,2,3]}) // key1=1%2C2%2C3 即 key1=1,2,3,数组被隐式转换为1,2,3
new URLSearchParams({"key1" : { age: 18 }}) // key1=%5Bobject+Object%5D 即 key1=[object+Object],对象被隐式转换为[object+Object]
//对于不支持`URLSearchParams` API 的浏览器可以使用`encodeURIComponent`替代
const getFormBody = (params) => {
const formBody = [];
for (const key in params) {
formBody.push(`${encodeURIComponent(key)}=${encodeURIComponent(params[key])}`);
}
return formBody.join("&");
}
getFormBody({"key1" : "value1", "key2": [1,2,3]}) // key1=value1&key2=1%2C2%2C3 即 key1=value1&key2=1,2,3, 数组被隐式转换为1,2,3
Query String只能传入String类型的字符串,如果我们希望传入复杂类型,前后端需要约定一种序列化参数的编码解码方案,如qs
// 在前端对参数编码
// 嵌套对象
Qs.stringify({{"key1" : { age: 18 }}}) // key1%5Bage%5D=18 即 key1[age]=18
// 数组
Qs.stringify({key1: [1,2,3]}) //key1%5B0%5D=1&key1%5B1%5D=2&key1%5B2%5D=3 即 key1[0]=1&key1[1]=2&key1[2]=3
// 在后端我们需要调用对应的解码函数
Qs.parse(`key1%5Bage%5D=18`) // {"key1":{"age":"18"}}
设置URL参数的例子
通过axios设置URL参数
const instance = axios.create({
paramsSerializer(params) {
return Qs.stringify(params);
},
});
// 或者
axios(`http://test.com?${Qs.stringify(params)}`)
通过fetch设置URL参数
fetch(`http://test.com?${Qs.stringify(params)}`)
Headers传参
Headers允许客户端和服务器通过request和response传递附加信息,主要用来描述资源或服务器或客户端的行为.
我们可以通过以下方式构造Headers
const headers = new Headers();
headers.append('Content-Type', 'application/json');
设置Headers参数的例子
通过axios设置Headers
const instance = axios.create({
headers: {
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'
},
paramsSerializer(params) {
return Qs.stringify(params);
},
});
// 或者
axios.defaults.headers.common['Authorization'] = AUTH_TOKEN;
axios.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type'] = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded';
通过fetch设置Headers
fetch('input', {
headers: {
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'
},
});
Body传参
Body表示HTTP消息中传输的数据字节,用于携带该请求或响应的有效负载正文。我们需要使用Content-Type表示发送数据的MIME类型
Content-Type表示形式为media-type;charset;boundary;如:
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=something
MIME类型通用结构为type/subtype, 由类型与子类型两个字符串中间用/分隔而组成。不允许空格存在。type表示可以被分多个子类的独立类别。subtype 表示细分后的每个类型。MIME类型对大小写不敏感,但是传统写法都是小写。如果MIME类型与实际发送的数据不符服务器会无法识别。
Media类型:
text: 纯文本数据,包括任何人类可读的内容、源代码或文本数据. 如text/plain,text/html,text/css, text/javascriptfont: 字体文件. 如font/woff,font/ttfmodel: 3D 对象或场景的模型数据. 如model/gltf-binary,model/gltf+json,model/objimage: 表明是某种图像。不包括视频,但包括动态图(比如动态 gif. 如image/gif,image/png,image/jpeg,image/webpaudio: 音频文件, 如audio/webm,audio/wav,audio/mp4video: 视频文件, 如video/webm,video/wav,video/mp4application: 任何不明确归入其他类型之一的二进制数据;将以某种方式执行或解释的数据或需要特定应用程序或应用程序类别才能使用的二进制数据。 如application/pdf,application/xml,application/jsonmultipart: 表示被分成几部分的文档类别,通常具有不同的 MIME 类型, 代表一个复合文档。 如multipart/form-data,multipart/encrypted
text/plain表示没有特定子类型的文本文档,同样,application/octet-stream表示没有特定或已知子类型的二进制文档。
请求常用的MIMEType:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
这应该是最常见的提交数据的方式了(设置form表单enctype为空或者设为application/x-www-form-urlencoded)
他编码方式类似Query String,数据被编码成以 & 分隔的键 - 值对,同时以 = 分隔键和值。非字母或数字的字符会被 percent-encoding, 这也就是为什么这种类型不支持二进制数据, (使用multipart/form-data代替)
如提交数据{name: 'ck', email: 'ck@test.com'}被编码为
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: test.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
name=ck&email=ck%40test.com
其他例子
{key1: 'value1'} // 编码为 key1=value1
{key1: 'value1'} // 编码为 key1=value1
{name: 'ck', email: 'ck@test.com'} // 编码为 name=ck&email=ck%40test.com
// 同Query String, 参数只能为百分比编码的字符串, 如果需要传递复杂类型,需要对其编码为字符串格式
{key1: [1,2,3]} // 编码为 key1=1%2C2%2C3 即key1=1,2,3
{key1: [1,2,3]} // 有的编码方案也会将其编码为 key1%5B0%5D=1&key1%5B1%5D=2&key1%5B2%5D=3 即 key1[0]=1&key1[1]=2&key1[2]=3
发送application/x-www-form-urlencoded类型请求的例子
使用表单
<form action="https://test.com" target="target" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded" method="post">
<div>
<label for="name">Enter your name: </label>
<input type="text" name="name" id="name" value="ck" required>
</div>
<div>
<label for="email">Enter your email: </label>
<input type="email" name="email" id="email" value="ck@test.com" required>
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</div>
</form>
使用Fetch
await fetch('https://test.com', {
method: "POST",
// 当body参数为URLSearchParams类型时,Content-Type被默认设为application/x-www-form-urlencoded
// headers: {
// 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
// }
body: new URLSearchParams({
name: 'ck',
email: 'ck@test.com',
})
})
使用Axios
axios({
method: 'post',
url: 'https://test.com',
// 当body参数为URLSearchParams或者字符串类型时,Content-Type被默认设为application/x-www-form-urlencoded
// headers: {
// 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
// }
data: new URLSearchParams({
name: 'ck',
email: 'ck@test.com',
})
});
multipart/form-data
由于编码的原因application/x-www-form-urlencoded并不支持二进制数据,所以如果上传的表单包含文件则需要此方式提交(设置form表单enctype为multipart/form-data)
他的编码方式是将每个值都作为一个数据块发送,并使用用户代理定义的分隔符(boundary)分隔每个部分。值在每个部分的 Content-Disposition 标头中给出。
如提交数据{name: 'ck', email: 'ck@test.com', avatar: <file>c968b3620bc26294fac5626d25ccd72d.jpg}被编码为
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: test.com
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundaryPj0HGKm8KjgzNzN7
------WebKitFormBoundaryPj0HGKm8KjgzNzN7
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="name"
ck
------WebKitFormBoundaryPj0HGKm8KjgzNzN7
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="email"
ck@test.com
------WebKitFormBoundaryPj0HGKm8KjgzNzN7
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="avatar"; filename="c968b3620bc26294fac5626d25ccd72d.jpg"
Content-Type: image/jpeg
<binary content>
发送multipart/form-data类型请求的例子
使用表单
<form action="https://test.com" target="target" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
<div>
<label for="name">Enter your name: </label>
<input type="text" name="name" id="name" value="ck" required>
</div>
<div>
<label for="email">Enter your email: </label>
<input type="email" name="email" id="email" value="ck@test.com" required>
</div>
<div>
<label for="avatar">Choose a profile picture:</label>
<input type="file" name="avatar" id="avatar" accept="image/png, image/jpeg">
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</div>
</form>
使用Fetch
const getFormData = (params) => {
const formData = new FormData();
for (const key in params) {
formData.append(key, params[key]);
};
return formData;
}
await fetch('https://test.com', {
method: "POST",
// 当body参数为FormData类型时,Content-Type被默认设为multipart/form-data
// headers: {
// 'Content-Type': 'multipart/form-data',
// }
body: getFormData({
name: 'ck',
email: 'ck@test.com',
avatar: <File>
})
})
使用Axios
axios({
method: 'post',
url: 'https://test.com',
// 当body参数为FormData类型时,Content-Type被默认设为multipart/form-data
// headers: {
// 'Content-Type': 'multipart/form-data',
// }
data: getFormData({
name: 'ck',
email: 'ck@test.com',
avatar: <File>
})
});
text/plain
对于text文件类型若没有特定的subtype,就使用text/plain, (设置form表单enctype为text/plain)。 即它意味着未知的文本文件。
如提交文本数据
name=ck
email=ck@test.com
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: test.com
Content-Type: text/plain;charset=UTF-8
name=ck
email=ck@test.com
发送text/plain类型请求的例子
使用表单
<!--
该表单会发送以下body
name=ck
email=ck@test.com
-->
<form action="https://test.com" target="target" enctype="text/plain" method="post">
<div>
<label for="name">Enter your name: </label>
<input type="text" name="name" id="name" value="ck" required>
</div>
<div>
<label for="email">Enter your email: </label>
<input type="email" name="email" id="email" value="ck@test.com" required>
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</div>
</form>
使用Fetch
await fetch('https://test.com', {
method: "POST",
// 当body参数为字符串类型时,Content-Type被默认设为text/plain
// headers: {
// 'Content-Type': 'text/plain',
// }
body: `name=ck\nemail=ck@test.com`
})
使用Axios
// 当body参数为字符串类型时,Content-Type被默认设为application/x-www-form-urlencoded,所以这里需要显示设置text/plain
axios({
method: 'post',
url: 'https://test.com',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'text/plain',
}
data: `name=ck\nemail=ck@test.com`
});
application/json
表示发送的数据是个JSON。
关于为什么不是
text/json或者text/javascript,https://bluesmoon.livejournal.com/227190.html I spoke to Douglas about this in the UK actually, and asked him this same question. His answer was that JSON is not really javascript (hence no text/javascript), and not really text (hence no text/). Also, the IANA is less likely to hand out text/ types.
如提交数据{name: 'ck', email: 'ck@test.com'}被编码为
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: test.com
Content-Type: text/plain;charset=UTF-8
{"name":"ck","email":"ck@test.com"}
发送application/json类型请求的例子
使用Fetch
// body并不支持传递JSON对象,也不会设置默认headers<https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Fetch_API/Using_Fetch#body>
await fetch('https://test.com', {
method: "POST",
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
}
body: JSON.stringify({
name: 'ck',
email: 'ck@test.com'
})
})
使用Axios
axios({
method: 'post',
url: 'https://test.com',
// 当body参数为JSON对象时,Content-Type被默认设为application/json
// headers: {
// 'Content-Type': 'application/json',
// }
data: {
name: 'ck',
email: 'ck@test.com'
}
});
其他Content-Type类型
其他类型被编码为如 video/mp4,image/png
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: test.com
Content-Type: <对应MIME类型>
<binary content>
发送其他Content-Type类型请求的例子
使用Fetch
await fetch('https://test.com', {
method: "POST",
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'image/png',
}
body: <Blob> // 参考 <https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Blob>
})
使用Axios
axios({
method: 'post',
url: 'https://test.com',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'image/png',
}
data: <Blob> // 参考 <https://axios-http.com/docs/req_config>
});
感谢阅读!!!